In the forex market, it is important for traders to know the various economic indicators and market news which move the market.
Those indicators and news can give you important data for your trading. In this second part of the post we will bring you three other essential market news, while you can read the first two on Top 5 Market News You Must Know (Part 1).
3. CPI (Consumer Price Index)
The CPI (Consumer Price Index) is a key determinant of the level of inflation in an economy. It gives an indication about the changes in the average prices paid by consumers for a basket of market goods. It is one of the most widely used inflation measure out of the various economic indicators.
Inflation is one of the key data Central Banks look at, to guide them in their interest rate and policy decisions. It is one of the Central Banks’ mandate to regulate inflation and it is a balancing act they have to do. But why?
We also have the PPI (Producer Price Index) which go hand in hand with CPI. PPI is different from the CPI in 2 aspects: Targeted goods and services and prices.
Targeted Goods and Services
The producer price index focuses on the whole output of producers in the United States which is extensive. The PPI tracksthe goods and services purchased by producers as inputs in their own operations or as investment, and also includes goods and services bought by consumers from retail sellers and directly from the producer. CPI on the other hand only tracks goods and services consume by urban US residents and include imports.
The Price of Goods and Services
PPI does not include sales and taxes incurred for the producer’s return as these does not benefit the producer. CPI on the other hand includes both sales and taxes as they directly impact the consumer, causing them to pay more for the goods and services they consume.
Both indexes show different aspects of the economy health though CPI maybe the main focus most of the times due to its nature of tracking direct impact on consumers.
When inflation is too high, it means prices of goods/services are rising too fast and becoming less affordable to the consumers. The consumer spending power will drop and eventually have a negative impact on the economy. One of the possible causes is a weakening currency, making it costlier to pay for foreign goods/services. A possible counter measure against high inflation is by raising interest rates. This will increase the value of the currency and making it less costly to pay for foreign goods/services.
When inflation is too low, it means prices of goods/services are rising too slowly and are hurting the revenue of businesses. One of the possible causes is a strengthening currency, making it costlier for other countries to buy the goods/services and lower the competitiveness of businesses. A possible counter measure against low inflation is by cutting interest rates. This will decrease the value of the currency and making it less costly for other countries to buy the goods/services. The other possible counter measures include quantitative easing and negative interest rates. The ultimate purpose is to weaken the currency.
Lastly, deflation (falling of prices) is something all Central Banks want to avoid. It means the country is not growing but regressing. Central Banks will usually take drastic actions in the face of deflationary risk. Their course of actions would likely be similar to the case of low inflation but in a greater magnitude.
For developed nations, the Central Banks will usually set the inflation target around 2%. For developing nations, the target is usually set around 4%.
Example: On the 9th November 2017, China announced their CPI and PPI which is ahead of the forecast of 1.8% and 6.6% at 1.9% and 6.9% respectively. This inches Aussie dollar as China is one of the biggest trading partner of Australia. Thus, any hawkish news for China usually boost Aussie dollar up.
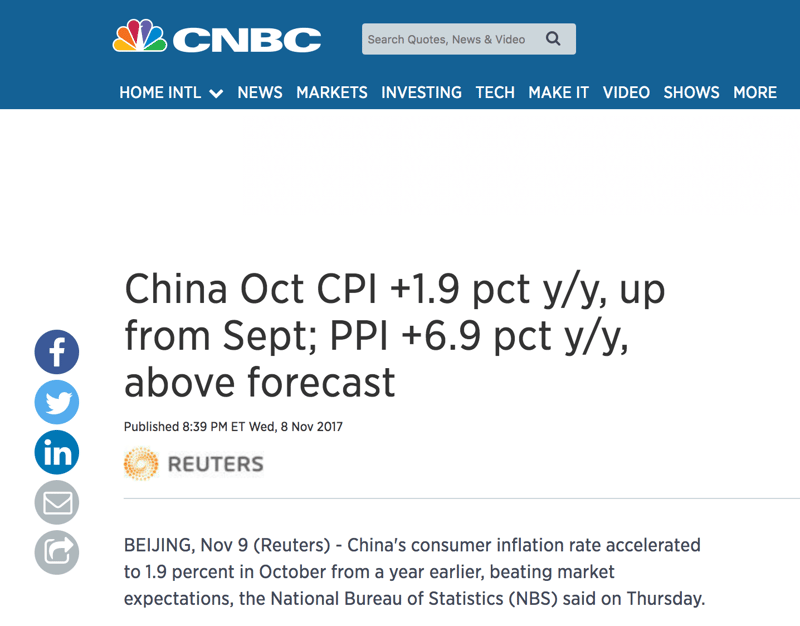
China's Increasing CPI and PPI, Source: CNBC - November 9, 2017
4. Employment/Jobs Data
Employment/Jobs data typically includes:
- Jobs growth
- Wage growth
- Unemployment rate
- Unemployment claims
The Jobs Growth figure is expressed as the gross number of jobs created in the American economy in the previous month. A job growth figure between 100,000 and 150,000 new jobs per month is considered to be the minimum level of job growth needed to mitigate the effects of new entrants to the workforce.
Average Hourly Earnings (Wage Growth) is the average amount employees make per hour in a given month. The Federal Reserve uses average hourly earnings in deciding whether to raise or lower interest rates.
The Unemployment rate of a country is one of the most influential indicator to reveal the well-being of an economy, especially to the Central Bank. A lower employment leads to interest rate reduction or unchanged as Central Banks aim to balance inflation with economic stagnation or decline and as such this affects traders extensively.
Unemployment Claims is the request made by an individual to the state government to receive temporary payments after having been laid off from a job. The United States Department of Labour keeps track of the number of weekly unemployment claims. These data are reported in the media as an indication of national and state economic health.
Labour statistics US ADP and NFP figures are also released alongside with unemployment rate each month with the NFP taking charge. However, sometimes the Average Hourly Earnings shadows over the unemployment rate figures especially during weather distortion which causes unemployment rate to dip as expected.
Example: One classic example of unemployment rate is the results of US after Hurricane Harvey and Maria in September which was a 33k job loss and unemployment rate of 4.2%, lowest since May 2001. Despite having a Non-farm payroll of a -33k which purely due to weather distortions, the focus on the unemployment rate caused the Dollar to rose.

The US Job Cuts, Source: The Wall Street Journal - October 6, 2017
5. Purchasing Manager Index (PMI)
The Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) is an indicator of the well-being of a particular sector of the economy. There are a few types of PMI that covers different sectors of the economy namely Manufacturing, Services, Construction, Composite etc. It is based on the 5 major indicators namely: new orders, inventory levels, production, supplier deliveries and the employment environment.
A PMI reading above 50.0 indicates expansion in the particular sector. On the other hand, a PMI reading below 50.0 indicates contraction.
There is also an early estimate PMI called flash PMI. It is designed to provide an accurate estimation ahead of the actual PMI. As the flash PMIs are among the first economic indicators shown each month, providing clues of changing economic conditions ahead of comparable government statistics, they can have a significant impact on the markets.
Example: The US Manufacturing production for October 2017 rebounded from hurricane-related disruptions. This is being confirmed as earlier signals from HIS Markit’s PMI data of 54.6 as compared to 52.4 in both August and September. This increase is the largest in production since February. As PMI is the first few economic indicators being announced. It is vital for traders to take note of the PMI so as to gauge the economic health of the economy.
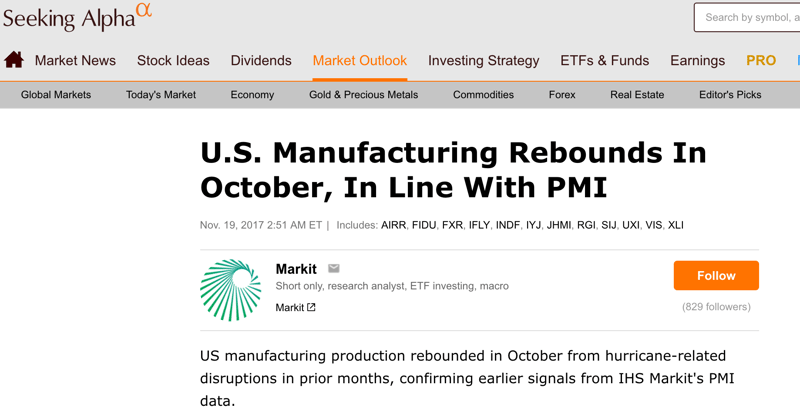
US Manufacturing Production Rebounds, Source: Seeking Alpha - November 19, 2017
In summary, economic indicators and news releases do not show the full picture as to whether a currency is going to strengthen or weaken, but they provide us reasonable benchmarks and references to make our trading decisions. How the market anticipates the release and how much does it differ from the actual release is where we can find good trading opportunities.
Market volatilities can be quite extreme during the announcement of important data or news. Traders must be aware of the potential risks and exercise prudent money management when trading the news.
Louis Teo
Market Strategist